Understanding of Fluorinated Polymers and Application to Materials.
Fluorinated polymers possess unique properties that distinguish them from hydrocarbon polymers. Although carbon-fuorine bonds have a signifcant dipole moment, fuoropolymers tend to form aggregates with low polarity. They exhibit a variety of properties and functions, including water and oil repellency. However, due to health concerns associated with certain amphiphilic fuoroalkyl compounds, regulations are increasingly restricting the use of specific monomer species. Therefore, it is essential to understand the properties of fuorinated polymers from a molecular perspective and to explore their potential as materials. We are focused on designing new fuorinated polymers and analyzing their structures and physical properties. We also develop a wide range of applications, from industrial materials to those used in medical settings, in collaboration with a company.


Cover Gallery
Development of Partially Fluorinated Polymers with High Performance at Low Fluorine Content
We have synthesized a novel copolymer composed of fluorinated vinyl ether and [1.1.1]propellane. Despite containing only 40 mol% fluorinated units, thin films fabricated from this polymer exhibit higher water and oil repellency than polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), a representative fully fluorinated polymer.
Highly Alternating Copolymer of [1.1.1]Propellane and Perfluoro Vinyl Ether: Forming a Hydrophobic and Oleophobic Surface with <50% Fluorine Monomer Content
Okuda. M.; Akiyama, M.*; Funahashi, K.; Masuda, J.; Kohata, A.; Nakagawa, S.; Kashiwagi, K.; Sugiyama, N.; Okazoe, T.; Kawaguchi, D.*
ACS Macro Lett. 2024, 13, 1383–1389.

Development of Novel Functional Fluorinated Polymers
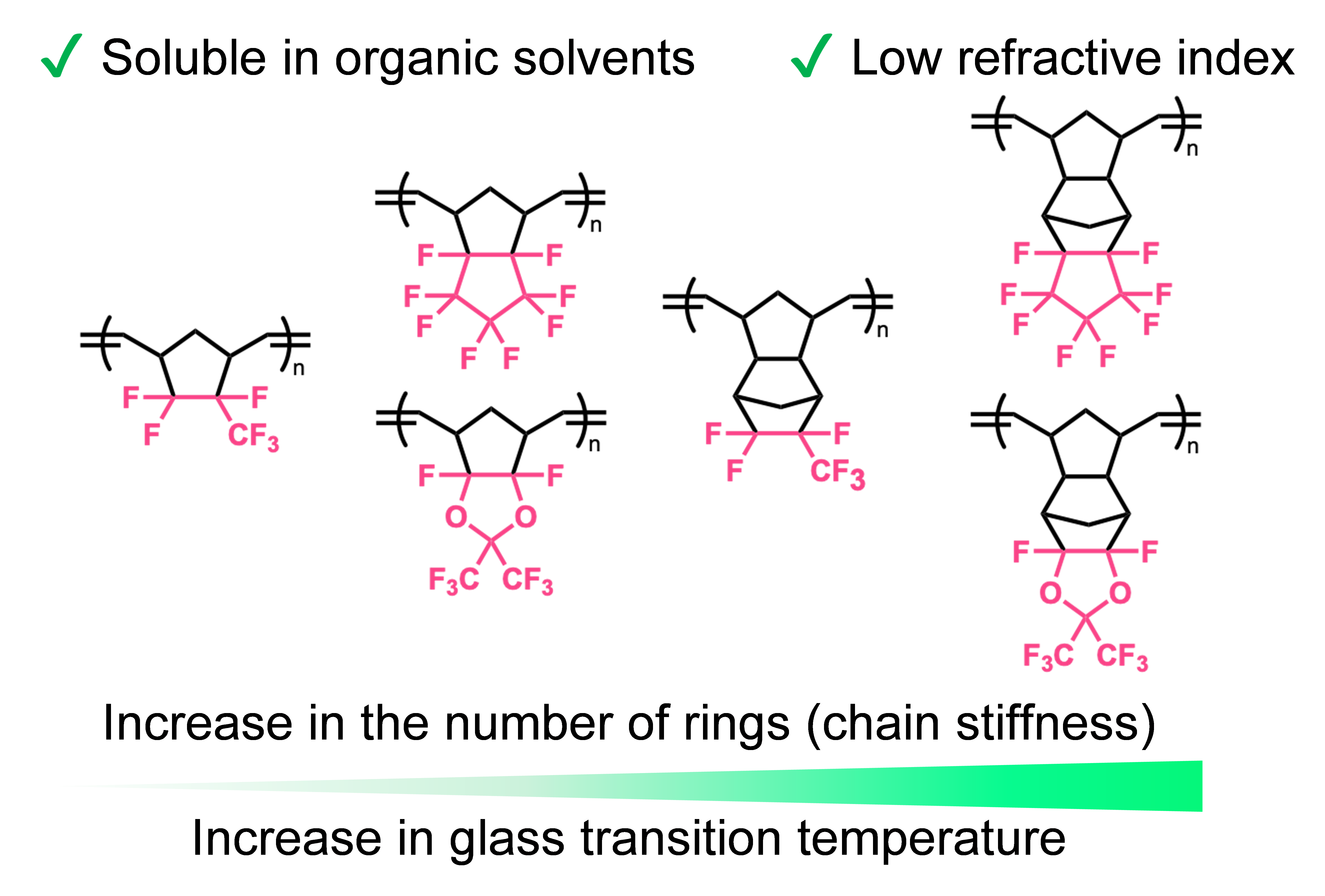
We have synthesized a new series of polynorbornenes with cyclic fluorinated skeleton. The resulting polymers ware found to exhibit the high transparency, high heat resistance, and low refractive index required for optical devices such as optical communications, while maintaining its solubility in non-fluorinated organic solvents. We also found that the bulkiness of the side groups plays an important role in their physical properties.
Polynorbornenes Bearing Cyclic Fluoroalkyl Side Groups for
Achieving High Glass Transition Temperature and Low Refractive
Index
Uno, M.*; Sugiyama, M.; Okazoe, T.; Kawaguchi, D.* Macromolecules 2025, 58, 3221–3230.
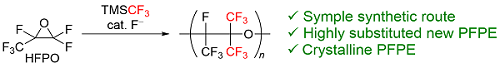
By copolymerizing hexafluoropropylene oxide (HFPO), a common monomer for fluoropolymers, with the Ruppert-Prakash reagent (TMS-CF3), we synthesized a fluorinated polyether incorporating multiple trifluoromethyl groups into its molecular chain. The resulting polymer exhibited a lower critical surface tension than polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE).
Synthesis of Crystalline CF3-Rich Perfluoropolyethers from Hexafluoropropylene Oxide and (Trifluoromethyl)trimethylsilane
Koyama, M.; Akiyama, M.*; Kashiwagi, K.; Nozaki, K.; Okazoe, T. Macromol. Rapid Commun., 2022, 43, 2200038.
Elucidation of the properties exhibited by fluoroalkyl groups and their understanding based on molecular images
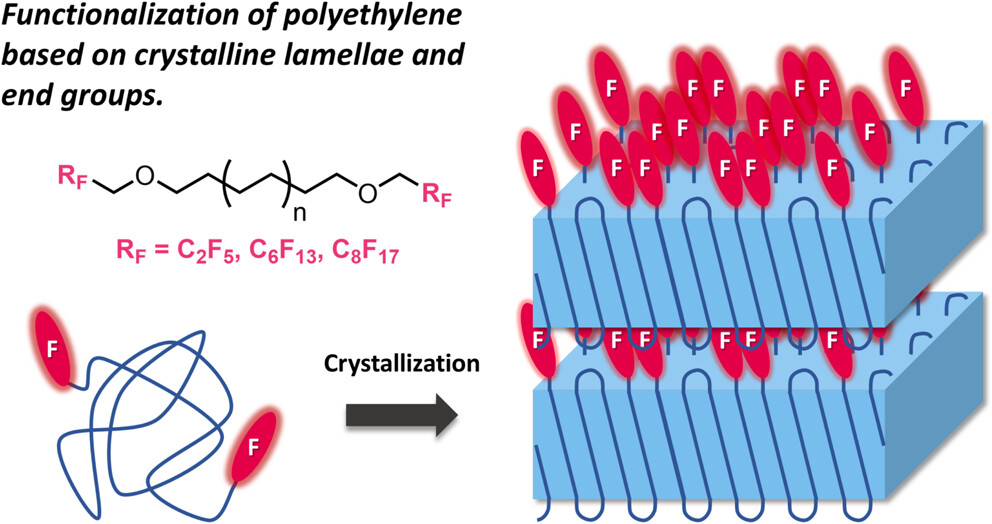
A linear polyethylene with fluoroalkyl groups at both chain ends was synthesized to investigate how the terminal groups influence the aggregation structure (crystalline lamellae) of polyethylene. It was found that the longer the fluoroalkyl chains, the more the crystals were stabilized at the crystal/amorphous interface. In addition, in thin films, the fluoroalkyl chains segregated to the surface, leading to a reduction in surface free energy. This behavior can be understood as a result of the more pronounced aggregation of the longer fluoroalkyl chains.
Fluoroalkyl Chain End Groups Regulating Crystal/Amorphous Interfaces of Semicrystalline Polyethylene Films
Tashiro, K.; Oda, T.; Mayumi, K.; Ikeda, O.; Koganezawa, T.; Hommura, S.; Okazoe, T.; Kawaguchi, D.*
Macromolecules 2025, in press.