Bioactive Substances
It is known that biological systems cannot distinguish between the size of hydrogen and fluorine atoms (the mimic effect). Additionally, fluorinated structures exhibit unique properties such as hydrophobicity, lipophilicity, and metabolic stability. In this regard, we aim to develop a novel drug delivery system by leveraging these characteristics of fluorinated molecules.
Synthesis and Applications of Biomolecules Designed for Cell Membrane Permeability
Peptides, proteins, and nucleic acids, which exhibit high specificity and affinity for target molecules, are promising as molecular-targeted drugs with fewer side effects and higher therapeutic efficacy compared to conventional chemically synthesized pharmaceuticals.
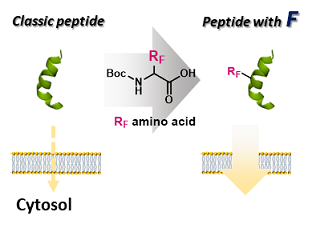
However, these highly hydrophilic molecules face a major challenge: their low cell membrane permeability, making it difficult to deliver them to intracellular disease targets. To address this issue, our laboratory has devised a strategy to enhance the membrane permeability of biomolecules by introducing fluorine-rich substituents (RF groups). These groups are highly rigid, exhibit strong hydrophobicity, and are expected to interact effectively with the phospholipids of cell membranes.

Kadota, K.; Kohata, A.; Sando, S.; Morimoto, J.*; Aikawa, K.*; Okazoe, T. RCS Adv. 2025, 15, 8189-8194.
Synthesis of Short Peptides with Perfluoroalkyl Side Chains and Evaluation of Their Cellular Uptake Efficiency
Kadota, K.; Mikami, T.; Kohata, A.; Morimoto, J.; Sando, S.; Aikawa, K.*; Okazoe, T. ChemBioChem 2023, e202300374.
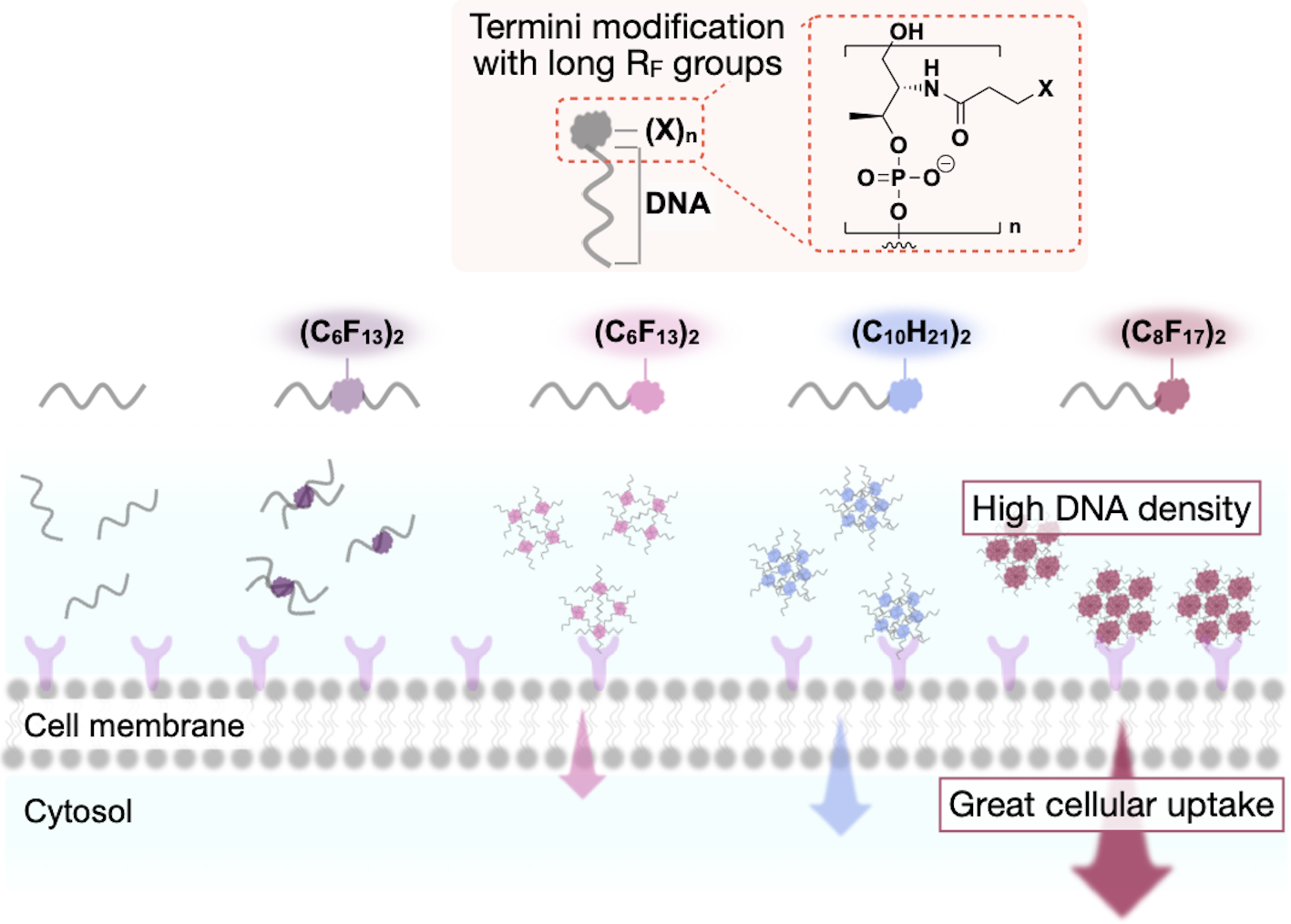
Fluorocarbon–DNA conjugates for enhanced cellular delivery: Formation of a densely packed DNA nano-assembly
Narita. M.; Kohata, A.*; Kageyama, T.; Watanabe, H.; Aikawa, K.*; Kawaguchi, D.; Morihiro, K.; Okamoto, A.; Okazoe, T. ChemBioChem 2024, e202400436.