植物生殖に関するその他の研究 / Other studies of plant reproduction
エピジェネティクス
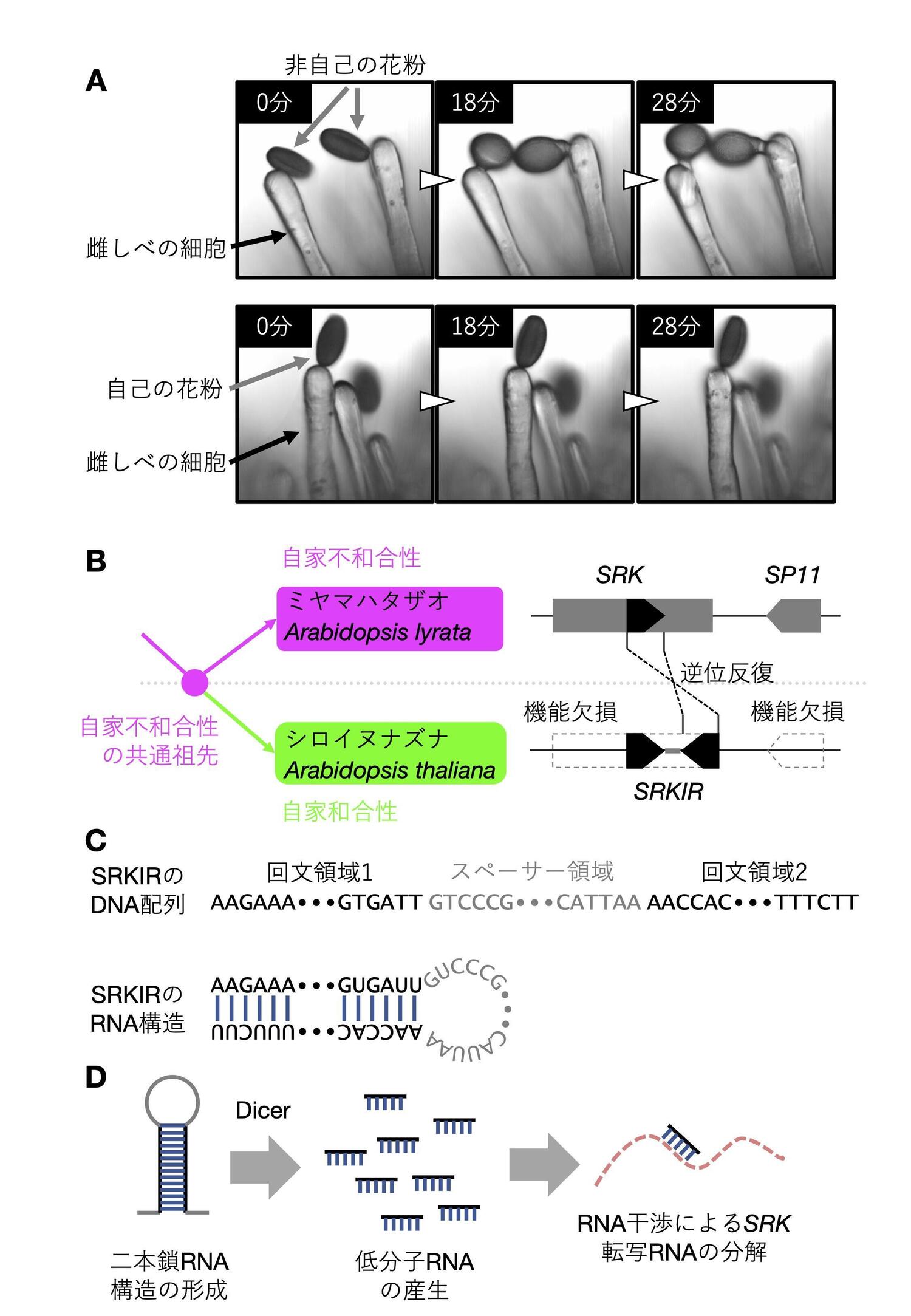
エピジェネティクスとはDNA配列そのものの変化ではなく、後天的なDNAやヒストンなどの化学修飾によって遺伝子発現を制御する仕組みを意味しています。近年このエピジェネティックな遺伝子発現制御が様々な生命現象を高次にコントロールしていることが明らかとなり注目を集めています。私たちは自家不和合性を決定する対立遺伝子間の優劣性を研究する過程で優性対立遺伝子の周辺から生産される低分子RNAが劣性の関係にある対立遺伝子のプロモーターをメチル化し、その発現を抑制することを発見しました。すなわち、メンデル遺伝として知られる古典的な「優劣性」という遺伝現象にもエピジェネティクスが関与する例があることを見出しました。現在はこの優劣性メカニズムのさらなる解明と植物に普遍的なエピジェネティックな発現制御機構の解明をめざして研究を進めています。
Epigenetics refers to the mechanism of controlling gene expression through chemical modifications of DNA and histones, rather than changes in the DNA sequence itself. In recent years, it has become clear that this epigenetic gene expression control plays a crucial role in regulating various biological phenomena at a higher level. In the process of studying the dominance relationship between opposing genes that determine self-incompatibility, we discovered that small RNAs produced around dominant opposing genes methylate the promoter of the recessive opposing gene, suppressing its expression. In other words, we found an example where epigenetics is involved in the classical genetic phenomenon of "dominance" known as Mendelian inheritance. Currently, we are conducting research to further elucidate this mechanism of dominance and the universal epigenetic expression control mechanism in plants.
*プレスリリース「メンデル遺伝の顕性を引き起こすDNAの「回文構造」を解明」より
性決定メカニズムの解明
花をつける植物の中で雌雄の株に分かれる種は約1万 5 千種あり、これらの雌雄は動物と同じように2種類の性染色体の組み合わせによって、その性別が決定されます。性染色体に は雌雄への発達を制御する性決定遺伝子がコードされていると考えられていますが、植物の性決定機 構はほとんど明らかになっていません。当研究室ではアスパラガスの性決定遺伝子MSE1を世界にさきがけて同定し、性分化に至る仕組みを明らかにしようとしています。